What are they, what’s the difference and why does it matter?
 |
| (http://suhanijain.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/09/food.jpg) |
Nutrients are what gives a person energy, repairs their body tissues,
and creates a strong physical body that grows and thrives (Sizer & Whitney,
2014). The human body needs varying
amounts of nutrients at different stages of life to survive and continue to
grow. During the first 10-15 years of
life the body is growing rapidly and changing, however, in a person’s middle to
late adulthood and senior years the body is in a maintenance phase (Herman et
al., 2014; De Jager et al., 2014). Some
nutrients are needed in large amounts and they are called macronutrients,
whereas other nutrients are needed in smaller amounts, thus they are called
micronutrients (Sizer & Whitney, 2014).
Of the six nutrients water, carbohydrates, protein, and fat are macronutrients,
and comparatively vitamins and minerals are micronutrients.
| (https://encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQ4S0gh9hnS0-g0cHFGEciqDG7Fy64JWy3f44VQz4drii8mCKEk_A) |
What do these nutrients do for the body? That is a great question with a very
important answer. Water is so important because
without it a person will die within a few days.
The human body is about 60 percent water allowing blood to cycle and
tissues to receive vitamins and minerals, in addition, the brain and lungs are
70-90 percent water respectively (Anspaugh, Hamrick, & Rosato, 2011; Sizer &
Whitney, 2014). Water can be consumed
through food, as well as liquid sources.
Therefore, one can see that if a person does not get enough water their
organs cannot function properly or for very long.
 |
| (http://www.healthproductsamerica.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Energy-system-basics.jpg) |
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins make the human body run because
they are the energy sources (Sizer & Whitney, 2014; Herman et al., 2014). In essence, they are the fuel that human’s
put into their bodies each day to get them from place to place, think, breathe,
and sustain their life (De Jager et al., 2014).
Some provide energy more rapidly, whereas others need to be processed
and converted into storage units for later use (Sizer & Whitney,
2014). Protein is an awesome energy
source because it is long-lasting meaning because it does not burn up quickly
and the amino acids within proteins help repair the body’s tissues when they
are used, stressed, and damaged (Sizer & Whitney, 2014; Anspaugh, Hamrick,
& Rosato, 2011). Think of protein as
the little carpenters running throughout the body while you sleep repairing the
walls of your house. They are pretty
impressive and
important.
 |
| (http://previews.123rf.com/images/cteconsulting/cteconsulting1108/cteconsulting110800002/10103320-An-image-of-a-handyman-who-is-a-jack-of-all-trades--Stock-Vector.jpg) |
 |
| (http://johnbarban.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/04/FoodGroups1.jpg) |
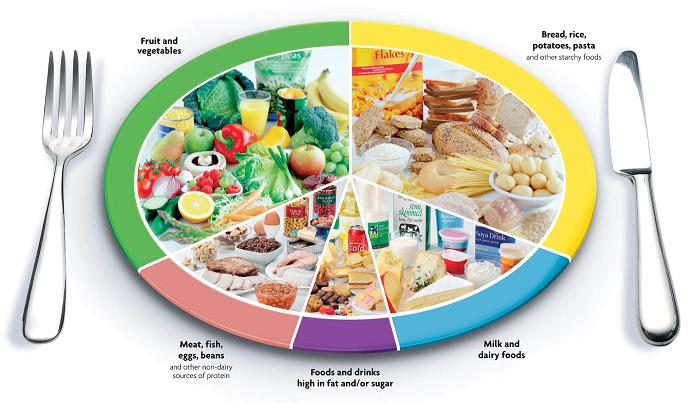
Sources of carbohydrates are fruits, vegetables, and grains. The more natural the better for the body
because they do not have fillers or additives added to them like boxed, prepared
food does. Fat is present in liquid form
of oils made from vegetables and nuts, within beans, nuts, meats, and
eggs. Some fat sources are healthier
because they are mono and polyunsaturated versus saturated (Sizer &
Whitney, 2014). The less saturation of
the molecules the better the source is for the human body. Furthermore, protein comes from meats, nuts,
legumes, and tofu. Protein sources that
are lean, meaning they have less fat in them, are healthier choices because too
much fat leads to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Lean turkey, ham, egg whites, nuts, and beans
are all great ways to take in protein.
 |
| (http://image.slidesharecdn.com/ms-pinepresentaionver04-091203153108-phpapp02/95/notes-nutrients-2-728.jpg?cb=1259854568) |
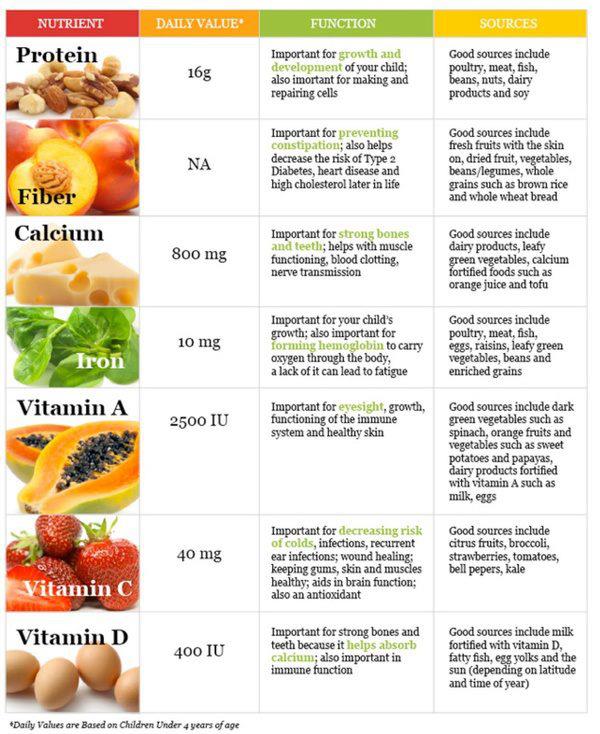
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients, but they make a
monumental difference to the function and immunity of the entire human body
from eyes to feet (Herman et al., 2014; Sizer & Whitney, 2014). These micronutrients regulate body functions
and serve as antioxidants preventing diseases in all areas of the body (Sizer &
Whitney, 2014). People can take their
body functions for granted, however, when sickness or disease rear their ugly
heads a person might start pumping in vitamins like C, D, A, B, E, and minerals
like potassium, iron, and calcium. If
you want your body to function well and live long give it the best energy
sources and the right amount of vitamins and minerals. Eat well and be strong.
References
Anspaugh, D. J.,
Hamrick, M. H., & Rosato, F. D. (2011). Wellness:
Concepts and applications (8th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Herman, D., Taylor Baer, M., Adams, E., Cunningham-Sabo, L.,
Duran, N., Johnson, D., & Yakes, E. (2014). Life course perspective:
Evidence for the role of nutrition. Maternal & Child Health Journal, 18(2),
450-461. doi:10.1007/s10995-013-1280-3
De Jager, C. A., Dye, L., Bruin, E. A., Butler, L.,
Fletcher, J., Lamport, D. J., & ... Wesnes, K. (2014). Criteria for
validation and selection of cognitive tests for investigating the effects of
foods and nutrients. Nutrition Reviews, 72(3), 162-179.
doi:10.1111/nure.12094
Sizer, F. & Whitney, E.
(2014). Nutrition: Concepts and controversies (13th
ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning.
No comments:
Post a Comment